The Role of Process Mining in Digital Transformation
Seongju Kim | May 7, 2019| 7 min read
Process mining bridges OT and IT, visualizes KPIs, and integrates AI in digital transformation.
Source: MITechNews
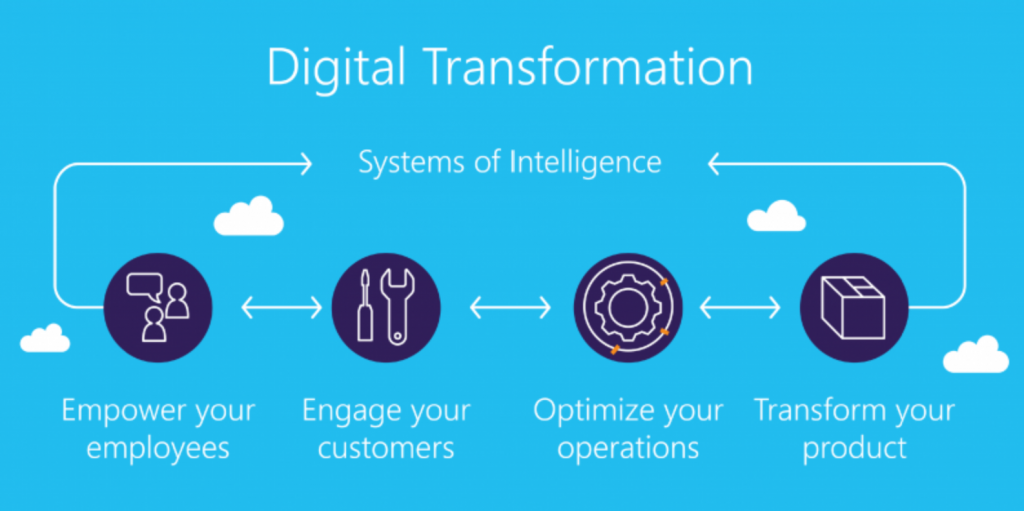
Recently, as discussions about digital business have been ongoing, the term “Digital Transformation (DX)” is frequently used in relation to corporate management. To understand this, it requires consideration of DX not only as a business buzzword but also as a concept. One needs to delve into what DX is (WHAT) and how it addresses problems (HOW). As one approach to this, let’s examine process mining.
Looking at the conventional definition of digital transformation, it refers to the endeavor of taking traditional business and using digital technologies such as cloud, big data, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and mobile to transform them into new services and business models.
This focus isn’t limited to companies that were born in the digital age like Google or Amazon. It encompasses traditional organizations in fields like manufacturing, finance, public sector, and retail, which are harnessing digital technologies to innovate their operations in novel ways and solve problems differently from the past.
With the technical validation of technologies like big data and artificial intelligence, represented by Hadoop and deep learning, the intrigue for business opportunities and strategic advantages they bring has grown among pragmatic executives. DX seems to offer a potential solution to their curiosity about how these technologies can be leveraged.
Of course, digital transformation can also become a vague management catchphrase without real substance. To overcome this, within the DX process, process mining plays a practical role by fulfilling two functions.
Firstly, it serves as a connector linking Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) to the higher-level strategy of an organization. In other words, it provides the capability to take log data generated at the OT or IT level and visualize business-oriented Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
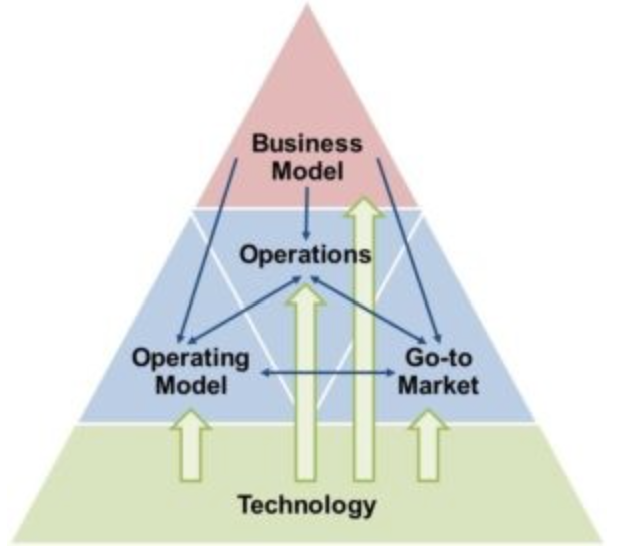
The Building Blocks of the Digital Transformation Pyramid
In the process of transforming traditional business areas into digital realms, there arises a necessity to adapt the control and monitoring methods for the entities constituting the current processes – organizations, customers, products, and operations – to align with the digital transformation. This has led to concepts like Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and Digital Twins, which merge the physical and virtual aspects. However, this goes beyond mere 3D simulations; there’s a need to comprehend and analyze real-world domain processes.
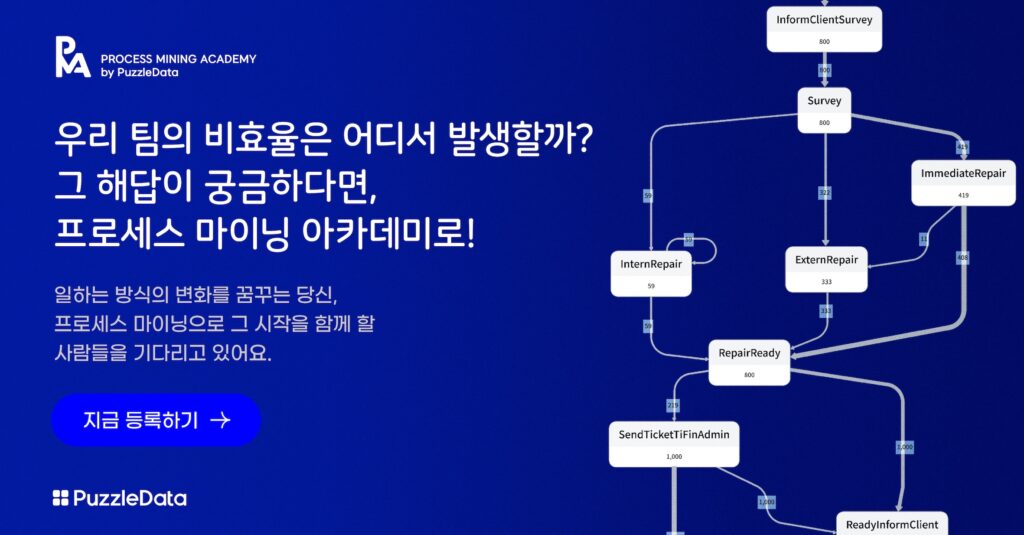
Process mining steps in to address this requirement comprehensively. It takes a holistic approach to the entire process, considering various elements such as organizations, equipment, tasks, schedules, and fixed attributes, and provides visualization capabilities for integrated business process models and related indicators.
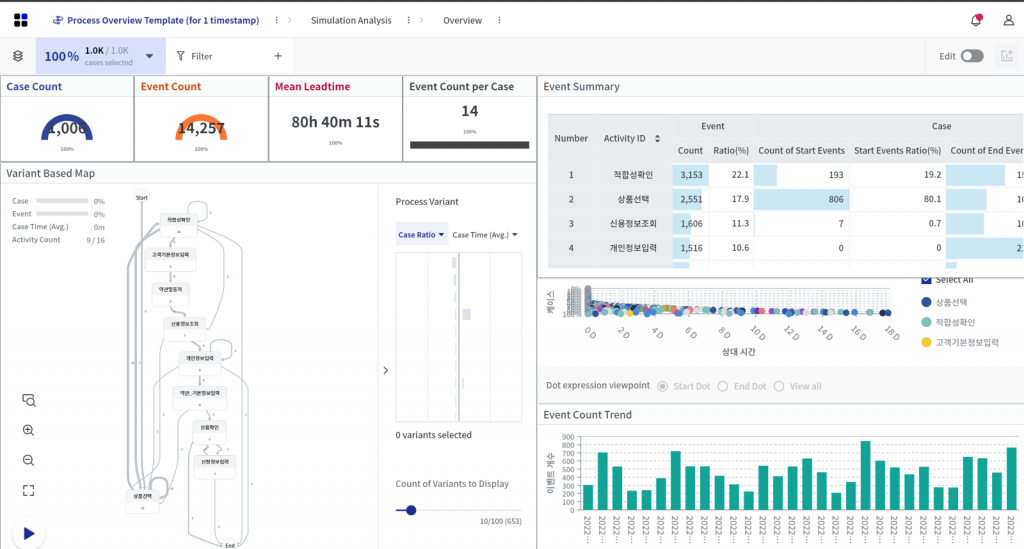
Process visualization using ProDiscovery’s KPI dashboard
Additionally, for parts of the existing process that involve manual operations and might be difficult to identify during the process mining analysis, the process of introducing digital transformation enables the identification of crucial bottlenecks or issues requiring significant improvements.
If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it (Peter Drucker)
Like the provided statement, Process Mining highlights the need for utilizing digital technologies like OT and IoT to measure activities related to tasks that may be missing from process models due to the absence of logged data. This awakening is distinct from merely computerizing and automating traditional methods; it involves viewing existing tasks from a fresh perspective and establishing criteria to measure the digitization occurring within the organization.
Through this, operational pain points within the operation domain can be identified from a higher strategic perspective. By reimagining processes, new business opportunities can be discovered through process innovation.
Secondly, the role of process mining in digital transformation involves the interpretation of real-world operations when applying artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to practical tasks. This is referred to as digital conversion.
In addition to the autonomous driving through image and voice recognition, as well as natural language processing, which have been actively driven by artificial intelligence, the extensive transactional data generated from various internal systems within enterprises such as ERP, MES, and various intranet web systems can be leveraged for AI-assisted decision-making in task execution, beyond the mentioned domains.

Source: Oracle
In this context, the problems that AI and machine learning technologies can address are numerical representations of vectors located in multidimensional spaces, forming a matrix world that machines can comprehend. To achieve this, real-world issues must be mapped onto the digital realm, also known as the digital twin, through a process of digital conversion.
For instance, to establish production and distribution plans related to a product, the stages involved in its production must be explicitly differentiated. Various environmental and operational variables for production are then input automatically through manual fieldwork or sensor data and sequentially stored in systems like MES or ERP. When aiming to utilize machine learning techniques for optimized production planning, defining the problem and inferring the results based on the existing data format tailored to OT and IT can prove challenging.
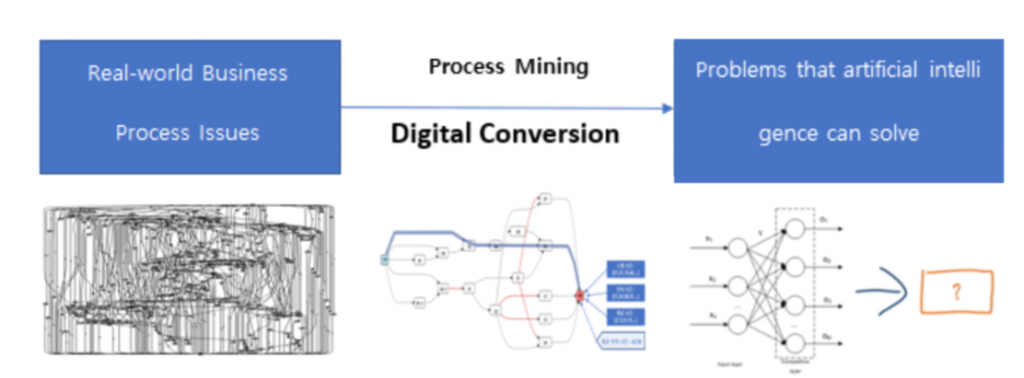
Process mining’s role in digital conversion
Process mining restructures existing transaction data from the perspective of the entire business process pipeline. In other words, attributes like tasks, workers, equipment, task duration, environmental variables, precedence relationships, and temporal characteristics existing in logs can be transformed into vectors of specific dimensions through the embedding of object data in the digitized process. This transformation enables machine learning algorithms to easily learn and infer, allowing for attempts at resource demand prediction, anomaly detection, segmentation, process optimization, and more.
By broadening the scope of real-world business problems and understanding and interpreting them from a process perspective, process mining paves the way for the application of artificial intelligence technologies. This process positions process mining as a tangible and practical means of achieving success in digital transformation.
References
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_transformation